-
Call for Papers for a Special Issue on “The Vietnam War and its Afterlife in Canadian Literature”
Canadian Literature seeks contributions for a guest-edited special issue on “the Vietnam War and its Afterlife in Canadian Literature.” As a descriptor, “the Vietnam War” signifies differently across spatial, temporal, and geographical boundaries. Some of its variants, metonymies, proxies, “sideshows,” and “postscripts” include: the American War in Vietnam, the Second Indochina War, the Cold War in Southeast Asia, the Secret War in Laos, the U.S. bombing of Cambodia, and the Cambodian Genocide. Collectively, these asymmetrical wars of empire contributed to the suffering of Vietnamese, Cambodian, Laotian, and Hmong people on a scale that Michel Foucault described in 1979 as “unprecedented in modern history.” These wars also disproportionately enlisted the labour of Black, Indigenous, and brown bodies to fight on the frontlines of the war in the name of securing the extractive economies of Southeast Asia for U.S.-led global capitalism.

Duffin’s Donuts in Vancouver, BC, run by former Cambodian refugees.
Canada’s involvement in the Vietnam War was marked by both complicity with and resistance to empire. On the one hand, Canada sent thousands of troops to Southeast Asia, provided the U.S. military with war material, and allowed the testing of chemical weapons on indigenous lands in Canada. On the other hand, Canada offered sanctuary to 30,000 U.S. war resisters and 60,000 Southeast Asian refugees, more refugees per capita than any other nation in the world. At local levels, Canadian groups mobilized in support of Southeast Asian refugees (e.g. Operation Lifeline) while others (the majority of the Canadian public polled at the time) were against the government’s asylum policies.
How might we begin to reconcile Canada’s humanitarian image of benevolence with its complicitous actions? How do the literary and cultural works that have been routed through Canada—including Denise Chong’s The Girl in the Picture, Kim Thuy’s Ru, Vincent Lam’s The Headmaster’s Wager, Madeleine Thien’s Dogs at the Perimeter, Dionne Brand’s What we All Long For, Johanna Skibsrud’s The Sentimentalists, Philip Huynh’s The Forbidden Purple City, Kathryn Kuitenbrouwer’s All the Broken Things, Tian Veasna’s Year of the Rabbit, Greg Santos’s Ghost Face, FONKi’s The Roots Remain, Jacqueline Hoàng Nguy?n’s The Making of an Archive, and Souvankham Thammavongsa’s How to Pronounce Knife, among others—engage with the recurring presence of the Vietnam War and its afterlife? To what extent does the Vietnam War as an imperial formation offer possibilities for rethinking the paradigm of Canadian literature as a field? How might this rethinking coalesce alongside contemporary movements in Asian, Black and Indigenous studies in Canada?
In particular, the journal welcomes bipoc, de-colonial, feminist, queer, trans, transpacific, and/or critical refugee studies approaches. Essays and contributions that blend the creative and the critical, as well as the theoretical and the autotheoretical, are welcomed and encouraged. Contributions need not be limited to the study of “literature” in its conventional sense.
Possible essay topics may include, but are not limited to, the following as they intersect with the theme of the Vietnam War and its Afterlife in Canadian Literature, broadly conceived:
- The Vietnam War (or variant) as an unsettling method or analytic
- Southeast Asian refugee memories, lifeworlds, and knowledges
- Black / Indigenous / Asian formations of the Vietnam War
- Soldiering, empire, and Canada as “minor empire”
- Militarism, slow violence, and ecological aftermaths
- Sponsorship, humanitarianism, and humanitarian violence
- Canadian civility, complicity, and “quiet complicity”
- Migrant affects: gratitude, anger, empathy, apathy
- Aesthetics, form, multimedia, and art
- Narratives of “good” and “bad” refugees
- Resettlement in the rural versus the urban
- French Indochina-Quebecois-Canada triangulations
- Parallel imperial formations (e.g. wars in Korea, Lebanon, Somalia, Syria)
- Refugee routes via militarized spaces (e.g. camps in the Philippines, Hong Kong, Canadian bases)
- Spaces of refuge and carcerality: boat, camp, asylum, prison, deportspora
- Sanctuary in relation to health, disability, and neurodiversity
- Refugee patriots and complicities
- Military industrial complex and war machines
- Food cultures, memory, and community
- Anti-racist, anti-colonial, bipoc solidarities and futures
All submissions to Canadian Literature must be original, unpublished work. Essays should follow current MLA bibliographic format (MLA Handbook, 8th ed.). Word length for articles is 7,000-8,000 words, which includes endnotes and works cited.
The journal recognizes that the current moment is full of challenges and precarities for the Canadian Literature community. We are open to considering submissions that go outside the bounds of conventional research articles, especially collaborative efforts and submissions from graduate students, early career scholars, artists, and members of the community. Please feel free to contact the journal editor, Christine Kim, at cl.editor@ubc.ca, or the special issue guest editor, Y-Dang Troeung, at y-dang.troeung@ubc.ca, to discuss ideas ahead of time. Submissions should be uploaded to OJS by the deadline of February 28, 2021. Our Submission Guidelines can be found at canlit.ca/submissions. General questions about the special issue may be directed to can.lit@ubc.ca.
-
EXTENDED: Call for Papers for a Special Issue on “Pandemics”
On March 11, 2020, the WHO officially declared the outbreak of COVID-19 to be a global pandemic. Similar to many other countries around the world, Canada closed its schools, borders, businesses, and other facilities and implemented measures such as social distancing and restricted gatherings as it tried to slow the spread of coronavirus and equip hospitals and other sites with sufficient amounts of personal protective equipment. Amongst other things, the pandemic has highlighted the challenges of balancing the physical and mental wellbeing of individuals and communities with the economic needs of individuals, families, and businesses. During this time, much of the labour of caring for the sick, elderly and other vulnerable populations, staffing grocery stores and meat production plants, harvesting crops, and delivering food has come from low-paid, racialized, and/or temporary migrant workers. And as we look towards the future, government and public health officials warn us that a second wave of the virus could take place since a vaccine has yet to be developed. The pandemic has dramatically changed our social and political landscapes; for example, we now routinely rely on new forms of technology to maintain intimate and professional relationships as we avoid physical contact with those outside of our ‘bubble.’

Photo by Laura Moss, Vancouver BC, April 2020
Over the past couple of months, our collective vocabularies have grown as we hear from public officials about the fact that we are now in ‘uncertain and unprecedented times’ and that we need to adjust to the ‘new normal.’ But what exactly do phrases like these mean? What role does storytelling play in dealing with the complexities of this moment? What historical precedents can we turn to? From Kevin Kerr’s play Unity (1918) to novels such as Emily St. John Mandel’s Station Eleven and Larissa Lai’s recent The Tiger Flu and films like Don McKellar’s Last Night, Tony Burgess’ Pontypool, and Jeff Barnaby’s Blood Quantum, issues around pandemics, contagion, and quarantine are not new to Canadian culture. How can Canadian literary and cultural production help us understand this moment, our shifting realities, and changing national and global imaginaries? Can we historicize our current crisis by, for example, turning to earlier discourses of disease, outbreaks, and the disciplining of racialized and Indigenous bodies? What new global understandings can we gain by comparing Canada to other nations as we all respond to this pandemic? How does the current pandemic exacerbate the precarities of academic life in the humanities and beyond? How have writers and artists configured pandemics in the past? In the present?
This special issue invites contributions that reflect critically upon pandemics and Canadian cultural production, which includes literature and many other forms of cultural expression. We are particularly interested in submissions that offer new forms of cultural critique and that investigate the cultural logics of pandemics. Possible topics and themes may include but are not limited to:
- Contagion, disease, and outbreaks
- The problem of borders
- Curtailment of transnational movement / migration
- Rise in nationalism and a return to protectionism
- Global capital and the postwar welfare state
- States of vulnerability with regards to age, gender, sexuality, class, race, precarious and mobile labour
- Dystopic imaginaries
- Reimagining space and spatial relations
- Affective dimensions of self-isolation and pandemics
- Temporalities such as the COVID-19 timeline, times of emergency, fear of the future, nostalgia for pre-pandemic time, the unmarked sense of time during isolation
- Racist group blame and the rise of anti-Asian violence
- New forms of creativity and expectations of productivity
- Online teaching and rethinking pedagogy
- Social justice in the time of pandemic
- Surveillance, technology, contact tracing, and public health
- Narrative medicine, rhetoric of health and medicine, and medical humanities
All submissions to Canadian Literature must be original, unpublished work. Essays should follow current MLA bibliographic format (MLA Handbook, 8th ed.). Word length for articles is 7,000-8,000 words, which includes endnotes and works cited.
The journal recognizes that the current moment is full of challenges and precarities for the Canadian Literature community. We are open to considering submissions that go outside the bounds of conventional research articles, especially collaborative efforts. Please feel free to contact the journal’s incoming editor, Christine Kim, at canlit.editor@ubc.ca, to discuss ideas ahead of time.
Submissions should be uploaded to OJS by the deadline of October 30, 2020. Our Submission Guidelines can be found at canlit.ca/submissions.
General questions about the special issue may be directed to can.lit@ubc.ca.
-
Call for Papers for a Special Issue on “Emerging Scholars, Redux”
In the five years since the first call for our inaugural Emerging Scholars issue, both the world and the field of Canadian literature have changed. A climate emergency has been declared. There has been a global rise in dangerous and exclusionary forms of nationalism. There have been wars and humanitarian crises. Large-scale public protest has become the norm. There has been a spotlight on the pervasiveness of sexual violence, intimidation, and bullying. Social media has both helped create communities and become a place for sharp dissent. We seem to be living in a state of sustained urgency. Urgent times prompt us to want to hear from emergent voices. The submissions for the first two Emerging Scholars issues (226, 228/9) dynamically showed the state of the field five years ago. How are researchers who will shape the field and its future engaging with it today?
How do emerging scholars critically engage with works of fiction, drama, poetry, intermedia, memoire, creative nonfiction, or adaptation today. Whether through a lens of environmental, energy, public, or medical humanities, or by way of critical race, decolonial, migration, refugee, or gender studies, or any other approach, what are newer scholars contributing to contemporary scholarship? Why study the history of literature and the historical contexts of cultural production and reception today?
We again turn to people who are (relatively) new to the field to call attention to new work in the field of Canadian literature. This issue will highlight the work of Emerging Scholars and showcase the directions the field is taking. We welcome submissions on any topic in English or French from senior graduate students, postdocs, and those who might consider themselves to be Emerging Scholars (we place no time limit on this category).
We are actively seeking submissions for this issue NOW, so please help spread the word!
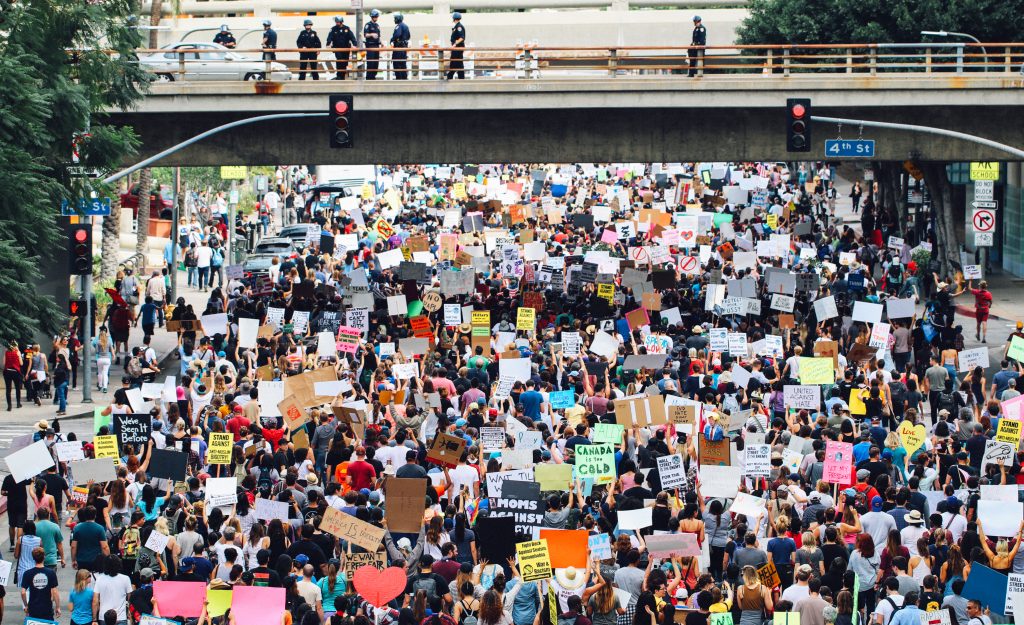

Photo by Alex Radelich on Unsplash
All submissions to Canadian Literature must be original, unpublished work. Essays should follow current MLA bibliographic format (MLA Handbook, 8th ed.). Word length for articles is 6,500-7,000 words, which includes endnotes and works cited.
Submissions should be uploaded to OJS by the deadline of January 31, 2020. Our Submission Guidelines can be found at canlit.ca/submissions.
Questions about the special issue may be directed to canlit.editor@ubc.ca or can.lit@ubc.ca.
-
Call for Papers for a Special Issue on “Decolonial (Re)Visions of Science Fiction, Fantasy, Horror”
Deadline extended to July 1, 2019 from May 15, 2019.
This special issue will address Black Canadian and Indigenous work in/with the genres of science fiction, fantasy, and horror, both genre fiction proper and slipstream fiction. While there has been quite a bit of attention to African American SF and increasingly to the burgeoning of genre fiction on the African continent, and while Indigenous SF has been growing and attracting more attention, there has not been as much attention to the relationships between Indigenous and Black SF in Canada or to the particular ways Canada’s settler colonial past and present inform the ways Black Canadian and Indigenous writers engage with science fiction, fantasy, and horror. How do Black and Indigenous writers respond to the different positions colonialism historically imposed on those who were subjected to alien abduction versus alien invasion? How do these genres re-present histories of slavery, genocide, displacement, and dispossession? While the dynamic between Black and Indigenous histories is at play across the Americas, as Nalo Hopkinson’s work illustrates nicely, we ask whether there is something specific about the Canadian iteration of that hemispheric history. What does it mean to engage in a comparison of Black and Indigenous writing in the genres from this location, the settler-colonial formation called Canada? How else might we think of the relations and relays between blackness and indigeneity in modes other than the comparative? How do the genres of science fiction, fantasy and horror attend to the historically triangulated relations among settler, Indigenous, and racialized immigrant peoples, including, for instance, Asian Canadians? What might be different about Asian Canadian engagement with this settler-colonial history? Whether in outer space, an alternate universe, a haunted house, or a mythic time, the worlds built in genre fiction seem to open up and provoke questions of how to both represent and transform the colonial conditions of our shared and still incommensurable world. How do Indigenous and Black Canadian writers working in or with these genres explore the possibilities for alternative kinds of social and political power—in other words, how do they take up the utopian impulses of conventional SF? This is the challenge of finding “new ways of doing things” that Nalo Hopkinson describes as the possibility in science fiction that is taken up by “the colonizee” as a form of critique.
Photo by Cassi Josh on Unsplash
We ask, further, how this comparative focus might allow for a critical engagement with Fredric Jameson’s claim that science fiction returns us to history by representing it as a speculative future, thus helping us to imagine ways past current political impasses. What does an Indigenous / Black novum look like? How do works of Afro- and Indigenous futurism also complicate the temporality of the novum by at times exploring what-could-have-been and what-always-has-been? In writing of recent African science fiction, Matthew Omelsky argues that it engages with a new form of biopolitics that he calls “neuropolitics,” by which he means the extension of power to “the control of memory and thought”; to what extent does Black / Indigenous SF exhibit a similar set of concerns?
Across these speculative, weird, and fantastic modes of storytelling, world-building and theorizing, how do Black and Indigenous authors grappling with the histories and the present of Canada find space to write within, persist within and demand the impossible?
For this special issue, we seek both scholarly essays on these questions and contributions from writers reflecting on their own work in/with these genres. In engaging with the questions outlined above, contributors might address, without feeling constrained by, the following specific themes:
- Land and colonization
- Contact and encounter
- The postcolonial and the decolonial
- Indigeneity and diaspora; sovereignty and belonging
- Comparisons between Canadian decolonial and US / diasporic / African / antipodean (re)visions
- Comparisons between Asian Canadian and Indigenous and/or Black-Canadian SF
- Contemporary ‘race science,’ scientific studies of ‘race’ and Black / Indigenous SF
- Speculative / racialized revisionings of gender and sexuality
- Critical utopias
- Temporality: how does Indigenous and Black Canadian SF do the ‘future’ differently?
- Enlightenment critique: scientific rationalism vs. non-European epistemologies
- Tensions between Indigenous design/technologies and those introduced from without
- Publishing media for genre fiction
- Film and graphica
- Monstrosity
- Haunting
- Possession and/or dispossession
- The different modalities of fantasy, SF, horror
- The apocalyptic
Special Issue editors: Lou Cornum, Suzette Mayr, and Maureen Moynagh
The deadline for submissions is May 15, 2019. Please consult canlit.ca/submissions for instructions on how to submit via Open Journal Systems. All papers submitted will undergo a formal peer review process through Canadian Literature. Essays should follow current MLA bibliographic format (MLA Handbook, 8th ed.). Word length for articles is 6,500-7,000 words, which includes endnotes and works cited. All correspondence will go through the CanLit office.
-
Call for Papers for a Special Issue on “Rescaling CanLit: Global Readings”
It is now commonly accepted that Canadian literature has become a global literature, implying that any understanding of textual localities is traversed by vectors that exceed, complicate, and extend the nation in physical, historical, and cultural ways. But the gaze is seldom reversed and little attention has been paid to the role of international scholarship in the current transformation and development of the field.
 How are Canadian texts read and circulated beyond the national borders? What is the place of Canadian literature in the institutional spaces of universities outside Canada? How do those transnational contexts negotiate the relationship between texts and readers? Are there defining differences in the ways non-Canadian scholars approach CanLit? How does transnational scholarship influence, challenge, enrich, and rescale Canadian literary production?
How are Canadian texts read and circulated beyond the national borders? What is the place of Canadian literature in the institutional spaces of universities outside Canada? How do those transnational contexts negotiate the relationship between texts and readers? Are there defining differences in the ways non-Canadian scholars approach CanLit? How does transnational scholarship influence, challenge, enrich, and rescale Canadian literary production?This special issue invites scholars of Canadian literature from around the globe to engage critically with any aspect of Canadian literary production, dissemination, or reception. Essays should implicitly bring to view the two-way direction of reading and writing Canadian literature globally, demonstrating the porosity of transnational scholarship as well as advancing innovative perspectives that may contribute to the rescaling of the field.
All submissions to Canadian Literature must be original, unpublished work. Essays should follow current MLA bibliographic format (8th ed).
Articles should be between 6500 and 7000 words, including endnotes and works cited.Submissions should be uploaded to Canadian Literature’s online submissions system (OJS) by the extended deadline of June 1, 2018.
The guest editor of this issue will be Eva Darias-Beautell of University of La Laguna, Spain.
-
Call for Papers for a Special Issue on “The Concept of Vancouver”
Vancouver, located on the unceded Coast Salish territories of the Musqueam, Squamish, Tsleil-Watuth, and Stó:l? First Nations, is an important urban nexus of art, literature, activism, and other forms of social and political organizing and expression within Canada. While its diversity has led to the emergence of well-developed cultural and political communities, writers and artists in Vancouver have also originated new and innovative collaborations across disciplinary boundaries. Sometimes this transdisciplinary work has been inspired by political causes, such as the environmentalist resistance to pipelines and old-growth logging or the Indigenous-led challenges to the effects of settler-colonialism (including land rights, discussions of Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women, Idle No More, ReMatriate, Red Power, and more) or the ongoing fights against neoliberalism and gentrification (especially of Vancouver’s Downtown Eastside). Sometimes this transdisciplinary work has been inspired by aesthetic initiatives, such as the McLuhan-inspired intermedia work (of the Western Front) in the 1960s and 1970s, or the experiments with interdisciplinary Surrealism in the 1970s and 1980s, or the fusion of various visual arts and literary communities across the past century. Authors and artists in the 1960s wrote about Vancouver as a marginal community, outside of the glare of international attention. Today, though, Vancouver’s situation on the west coast as a vibrant hub in a trans-Pacific network of overlapping business and cultural industries demands a reconceptualization of the city that reflects its overwhelming connectedness. For better and for worse, the city has become a cultural capital. Papers are encouraged to address any combination of the arts, literatures, and politics of Vancouver, and the interconnections these have with other scales of engagement, including the national and planetary issues in which Vancouver participates.
This special issue invites essays that examine the representation of Vancouver in art and literature, that consider individual authors and artists, that explore the state of aesthetic communities (visual, literary, architectural, filmic, etc.) in the city, or that address the confluence of politics and aesthetics. We are particularly interested in papers that explore links between art and resistance, art and the archive and collective/institutional memory, art in the neoliberal gentrification of the city and housing crises, and art and settler-colonial histories and decolonization efforts. We are also interested in papers that consider avant-garde groups and affiliations (such as TISH, the hippy and Beat poets of the 60s and 70s, Press Gang, the Vancouver School of photo-conceptualists, and the Kootenay School of Writing, amongst others), contemporary urban space, the politics of architecture, micro-literary histories, and transnational or transborder considerations. Canadian Literature publishes essays on fiction, poetry, non-fiction, drama, and inter-genre collaborations.
All submissions to Canadian Literature must be original, unpublished work. Essays should follow the bibliographic format of the MLA Handbook, 8th ed. Articles should be between 6,000 and 7,000 words, including endnotes and works cited. Submissions should be uploaded to Canadian Literature’s online submissions system (OJS) by the deadline of August 31, 2017. See our submission guidelines for details. Expected publication date of the issue is fall 2018.
Guest editors of this issue will be Gregory Betts, Julia Polyck-O’Neill, and Andrew McEwan.
-
Call for Papers for a Special Issue on “Ecocriticism after Ecocriticism”
In the last two decades, ecocriticism has become thoroughly established in Canadian literary studies. Environmental approaches to Canadian literature have transformed conventional ideas of nature and natural aesthetics; reshaped understandings of places, regions, animals, and labour; and imbued scholarship and teaching with political urgency. What in the 1990s was a new and insurrectionary critical development has become a profusion of conferences, articles, and books about Canadian environmental writing. Some twenty-five years after the term “ecocriticism” first appeared in this journal, and one hundred issues after Laurie Ricou’s “So Big About Green” editorial, the field is institutionally robust, eclectic in subject and method, and theoretically sophisticated—but also due for critical re-examination. Ongoing public controversies over tankers and hydroelectric dams, the continuing infringement of Indigenous sovereignty, the economic and political sway of the Alberta oil sands, and the increasing effects of anthropogenic climate change make a reconsideration of ecocriticism all the more pressing. Studies as different from each other as Timothy Morton’s Ecology without Nature: Rethinking Environmental Aesthetics (2007) and Jedediah Purdy’s After Nature: A Politics for the Anthropocene (2015) have attempted to dispense with inherited environmental ideologies in favour of critical, political, and aesthetic categories more appropriate to a radically changing biosphere. Where, then, is Canadian environmental literature after nature? And where are Canadian literary studies after ecocriticism?
 This special issue invites essays that examine the state of ecocriticism in the Canadian context, that take original environmental approaches to Canadian writing, that explore creative responses to environmental destruction and growth, and that consider the functions of literature and criticism in the neoliberal Anthropocene. How do we imagine environmental aesthetics today and for the future? What do nature writers of the past, as well as the present, have to tell us in the time of pipelines, protests, and protection of the land? We are especially interested in essays that suggest new paradigms for understanding the shape and politics of “nature” in the literatures of Canada. Comparative, multilingual, and transnational approaches, or other modes that emphasize the plurality of ecologies and natures in Canada, are particularly welcome. Articles that do more than examine a single text in light of environmental theories are encouraged. We publish essays on fiction, poetry, non-fiction, drama, and inter-genre collaborations. Contributors are invited to imagine new modes of ecocritical inquiry and to examine Indigenous ecologies and the decolonizing possibilities of environmental criticism. Studies of environmental literature from all historical periods are welcome.
This special issue invites essays that examine the state of ecocriticism in the Canadian context, that take original environmental approaches to Canadian writing, that explore creative responses to environmental destruction and growth, and that consider the functions of literature and criticism in the neoliberal Anthropocene. How do we imagine environmental aesthetics today and for the future? What do nature writers of the past, as well as the present, have to tell us in the time of pipelines, protests, and protection of the land? We are especially interested in essays that suggest new paradigms for understanding the shape and politics of “nature” in the literatures of Canada. Comparative, multilingual, and transnational approaches, or other modes that emphasize the plurality of ecologies and natures in Canada, are particularly welcome. Articles that do more than examine a single text in light of environmental theories are encouraged. We publish essays on fiction, poetry, non-fiction, drama, and inter-genre collaborations. Contributors are invited to imagine new modes of ecocritical inquiry and to examine Indigenous ecologies and the decolonizing possibilities of environmental criticism. Studies of environmental literature from all historical periods are welcome.All submissions to Canadian Literature must be original, unpublished work. Essays should follow the bibliographic format of the MLA Handbook, 7th ed. Articles should be between 6,000 and 7,000 words, including endnotes and works cited. Submissions should be uploaded to Canadian Literature’s online submissions system (OJS) by the deadline of April 15, 2017. See our submission guidelines for details.
This issue will be edited by Nicholas Bradley and Laura Moss.
Questions about the special issue may be directed to can.lit(at)ubc.ca.
-
Indigenous Literature and the Arts of Community
Deadline extended to June 30, 2016 from March 15, 2016
This special issue of Canadian Literature was inspired by the inaugural gathering of the Indigenous Literary Studies Association (ILSA), entitled “The Arts of Community,” which was held at Six Nations of the Grand River in October 2015. Seeking to catalyze and continue the conversations developed at that event, Canadian Literature invites submissions that explore new ways of thinking about Indigenous literary arts and community engagement.
We invite submissions by scholars, knowledge-keepers, artists, and community members that consider questions pertaining to community and Indigenous literature. We welcome academic papers, as well as creative critical pieces in alternative formats, for potential inclusion in a print issue of the journal and/or an affiliated online resource hub at canlit.ca. We are particularly interested in work that pursues strategies for moving beyond academic lip-service regarding “community consultation,” which too often replicates colonial power structures, and instead discusses methods of building relationships among scholars, artists, educational institutions, and Indigenous communities and nations based on reciprocity and respect. We therefore solicit submissions that engage with Indigenous literary arts to consider how research can become more accountable to the interests, concerns, and intellectual pursuits of Indigenous communities. Imagining literary creativity expansively, we welcome work that engages with literature, film, theatre, storytelling, song, hip hop, and other forms of narrative expression.
While open to all submissions dealing with Indigenous literary arts, we encourage work that engages with the following topics:
- the reciprocal influences of the arts on the meaning of “community” and of communities on the meaning of “art”
- the role of narrative arts in depicting, defining, addressing, and creating Indigenous communities
- the role of Indigenous communities in refining, expanding, and challenging understandings of art
- the responsibilities of artists and/or scholars to the communities of which they are part and to the communities addressed by and in their work
- the ethics of mobilizing and/or demobilizing community-specific Indigenous knowledge in scholarship or art
- the capacity of methodologies and practices prioritized in Indigenous literary studies to serve the needs of Indigenous communities
Given the significance of place to Indigenous understandings of community, and in acknowledgement of the territories in which the inaugural gathering of ILSA was held, we also invite work dealing with Haudenosaunee narrative arts, the literary history (and future) of Six Nations, and the legacy of E. Pauline Johnson Tekahionwake.
The deadline for submissions is March 15, 2016. All papers submitted will undergo a formal peer review process through Canadian Literature. Essays should follow current MLA bibliographic format (MLA Handbook, 7th ed.) Maximum word length for articles is 6500 words, which includes endnotes and works cited.
-
Asian Canadian Critique Beyond the Nation
NEW DEADLINE: January 1, 2016.
Asian Canadian critique has conventionally unfolded within nationalist frameworks. From important historical events such as the Chinese Head Tax, Japanese Canadian Internment, and the Komagata Maru Incident, to ongoing struggles over multiculturalism and global migrations, Asian Canadian critique has tended to emphasize the role of the nation-state in the marginalization of racialized populations. This approach has been central to the anti-racist pedagogy of the field, and has been deeply nurtured by its close ties with cultural communities, activists, and social movements. Yet the nationalist framing of Asian Canadian critique has also reinscribed citizenship and national belonging as the basis of political desire, thereby drawing the field back into the assimilatory impulses of multiculturalism.
This special issue invites contributors to reimagine Asian Canadian critique beyond the national(ist) imaginary. With its long-standing focus on racialization and marginalization within the nation-state, Asian Canadian critique is in a unique position to dismantle rather than reinforce national epistemologies. Historically, Asian Canadian communities were produced through global migrations that took place in the shadow of British and American empires, and its nationalist aspirations have unfolded both with and against these loyalties. More recently, Asian Canadians have appeared within the national imaginary in various ways as refugees and undocumented migrants, and as international students and bearers of global capital. By framing Asian Canadian critique as a transnational problematic, we counter-balance the field’s tendency to focus on Canada with the question,
What is the Asian in Asian Canadian?
In posing this query, we engage with the Asian as category, identity, representation, and a site of affective identification and disidentification.This special issue invites essays that reflect critically on existing frameworks in Asian Canadian critique and repositions the field in relation to trans-Pacific studies, world systems critique, comparative empires, inter-Asia cultural studies, global indigeneity, the global South, and other paradigms. We are especially interested in essays that question the coherence of Asian Canadian critique, not to mention Asian Canadian objects and topics, through comparative, multilingual, and transnational approaches that destabilize rather than reinforce national epistemologies.
All submissions to Canadian Literature must be original, unpublished work. Essays should follow current MLA bibliographic format (MLA Handbook, 7th ed.). Maximum word length for articles is 6,500 words, which includes endnotes and works cited.
Submissions should be uploaded to Canadian Literature’s online submissions system (OJS) by the deadline of January 1, 2016.
Questions about the special issue may be directed to can.lit(at)ubc.ca.
La critique canado-asiatique au-delà du prisme national
Éditeurs invités: Chris Lee, Christine Kim
Le paradigme nationaliste a longtemps dominé le champ de la critique canado-asiatique. Devant des faits historiques tels que la taxe d’entrée imposée aux immigrants chinois, les camps d’internements de Canadiens d’origine japonaise, l’incident du Komagata Maru, et face aux débats actuels suscités par le multiculturalisme et les mouvements migratoires internationaux, la critique canado-asiatique a souvent eu tendance à mettre l’accent sur le rôle de l’État-nation dans la marginalisation des populations d’origines étrangères. Cette approche a sans contredit été déterminante pour la constitution d’un discours pédagogique anti-raciste, et a été nourrie par ses liens étroits avec les communautés culturelles, le militantisme et les mouvements sociaux. Pourtant, le point de vue nationaliste de la critique canado-asiatique a également eu pour effet de réinscrire la citoyenneté et l’appartenance nationale parmi les principes fondamentaux de l’aspiration politique, renouant du même coup avec les anciens réflexes d’assimilation du multiculturalisme.
Ce numéro spécial se veut une invitation à repenser la critique canado-asiatique au-delà de l’imaginaire national(iste). En raison de l’attention qu’elle a longtemps accordée aux phénomènes de racialisation et de marginalisation à l’intérieur de l’État-nation, la critique canado-asiatique se trouve dans une position privilégiée pour questionner — plutôt que conforter — les épistémologies nationales. Historiquement, les communautés formées par les Canadiens d’origine asiatique sont issues des migrations produites dans la foulée des empires américains et britanniques; leurs aspirations nationalistes se sont ainsi manifestées à la fois avec et contre ces allégeances. Plus récemment, les Canadiens d’origine asiatique ont été diversement représentés dans l’imaginaire national, tantôt comme réfugiés ou migrants sans papiers, tantôt comme étudiant internationaux ou grands investisseurs. En inscrivant la critique canado-asiatique à l’intérieur d’une problématique transnationale, nous souhaitons faire contrepoids à la tendance consistant à se focaliser uniquement sur le Canada et à chercher à définir asiatique dans l’expression « canado-asiatique ». Ce numéro spécial est une invitation à interroger le terme asiatique à la fois en tant que catégorie, identité, représentation, objet d’une identification affective ou de son rejet.
Nous sollicitons des articles susceptibles de jeter un regard critique sur les traditions ayant contribué à l’essor de la critique canado-asiatique et plaidant pour un repositionnement de cette dernière à la lumière des travaux actuels dans le champ des études sur le Pacifique, de la critique des systèmes mondiaux, des études comparatives des impérialismes, des études culturelles inter-asiatiques, de l’indigénéité mondiale, du global south ou de tout autre paradigme. Nous sommes particulièrement intéressés par les articles remettant en question l’apparente uniformité de la critique canado-asiatique, ainsi que des objets qui lui ont traditionnellement été associés, à travers des approches comparatistes, plurilingues et transnationales susceptibles d’ébranler plutôt que renforcer les épistémologies nationales.
Canadian Literature ne publie que des articles originaux et inédits. Les articles — d’environ 6500 mots (notes et références bibliographiques comprises) — doivent respecter le style de citation MLA.
Prière de soumettre votre texte via le site de Canadian Literature (OJS) avant le 1er janvier 2016.
Pour toute question concernant ce numéro spécial, veuillez contacter can.lit(at)ubc.ca.
-
Emerging Scholars
Deadline: December 7, 2015
What is new in the study of Canadian literature? We turn to people who are (relatively) new to the field to ask this important question. This issue will highlight the work of Emerging Scholars and showcase the directions the field is taking. We welcome submissions on any topic from senior graduate students, postdocs, and those who might consider themselves to be Emerging Scholars (we place no time limit on this category). What better way to usher in a new editor than with a new scholars issue?
We are actively seeking submissions for this NOW, so please help spread the word!
All submissions to Canadian Literature must be original, unpublished work. Essays should follow current MLA bibliographic format (MLA Handbook, 7th ed.). Maximum word length for articles is 6,500 words, which includes endnotes and works cited.
Submissions should be uploaded to OJS by the deadline of December 7, 2015.
Questions about the special issue may be directed to can.lit(at)ubc.ca.
Numéro spécial consacré aux chercheurs émergents
Quels sont les nouveaux débats et les nouvelles perspectives qui animent les études sur la littérature canadienne? Nous invitons particulièrement les jeunes (et les moins jeunes) chercheurs à proposer leurs réponses à cette question importante et à indiquer des pistes pour éclairer les tendances actuelles de la recherche. Doctorants, post-doctorants et chercheurs émergents (nous n’attribuons aucune limite temporelle précise à cette catégorie) sont invités à soumettre des textes sur tout sujet touchant la littérature canadienne. Quoi de mieux qu’un numéro spécial rassemblant les travaux de nouveaux chercheurs pour marquer les débuts d’une nouvelle éditrice?
Date limite : 7 décembre 2015. Les soumissions sont les bienvenues dès MAINTENANT. Passez le mot!
Pour toute question concernant ce numéro spécial, veuillez contacter can.lit(at)ubc.ca.
